Recently, Professor Du Zuliang reported the methods for solving the problem of low light efficiency caused by the influence of the internal waveguide mode on the quantum dot light emitting diode (QLED). The PEDOT:PSS hole injection layer of one dimension and two dimensional grating structure was constructed by using nano-imprint technology, and the patterned QLED device was constructed. The optical performance of the QLED device is enhanced by restraining the waveguide mode, and the external quantum efficiency (EQE) of the device is improved by 21%. The research work is published in Nanoscale, 2018, 10.1039/C8NR02082E (SCI, IF=7.367).
Http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/nr/c8nr02082e#! DivAbstract
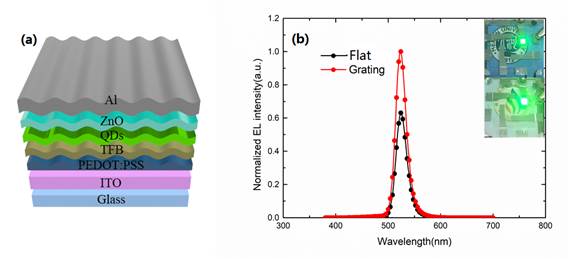
Figure(a)Schematic of flat and grating device structure of QLED in this work.(b)Normalized EL spectra. The insets depict the photographs of the fabricated QLED.
Extracting light from quantum dot light emitting diodes (QLEDs) by applying optical–functional nanostructures inside and outside the devices is essential for their commercial application in illumination and displays. In this paper, we demonstrate the highly effective extraction of waveguided light from the active region of QLEDs by embedding internal grating patterns fabricated using a nanoimprint lithography technique. The grating couples out waveguide mode power into the substrate without changing the device’s electrical properties, resulting in an increase in both the external quantum efficiency and luminous efficiency for a green QLED from 11.13% to 13.45%, and 29 010 cd m−2 to 44 150 cd m−2, respectively. The observed improvement can be ascribed to the elimination of the waveguide mode by the grating nanostructures introduced in the device. Furthermore, the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulation also demonstrated that the power loss due to the waveguide mode was reversed. The results indicate that internal nano-scattering pattern structures are attractive for enhancing the out-coupling efficiency of QLEDs.