Recently, Lin Song Li's group published an article entitled as “Synthesis of highly stable CuInZnS/ZnS//ZnS quantum dots with thick shell and its application to quantitative immunoassay” inChemical Engineering Journal. Article link:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894718307186?via%3Dihub
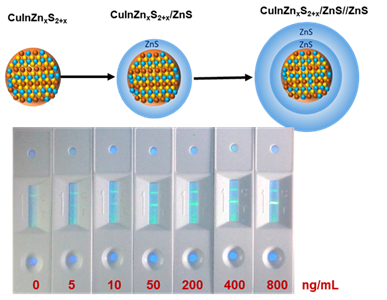
CuInZnxS2+x(CIZS, x=1) have been used as cadmium-free core materials to synthesize CIZS based core/shell quantum dots (QDs). As large as 7.8 ± 1.2 nm CIZS/ZnS//ZnS quantum dots with an average of 3.1 nm shell were synthesized successfully by introducing extra Zn precursor to CIZS cores, two-time separate shell growth process, and continuous long time replenishment of shell precursor. This process reduced the lattice mismatch between the core and the shell, also suppressed the core/shell interfacial defects and increased the PL QYs. Therefore, this newly developed approach solved the problem in the past that the shell of the CIZS/ZnS QDs was hard to be coated to realize the thick shell growth, and obtained by far the thickest shell and the largest particle size of CIZS related core/shell QDs with PL QYs of more than 70%. Such thick shell CIZS/ZnS//ZnS core/shell QDs had high stability and high quantum yields. Compared with the thin shell CIZS/ZnS QDs, the thick shell CIZS/ZnS//ZnS QDs still showed excellent PLQY (up to 58%) and stability in different environment after transfer to aqueous solution. We adopted the thick shell cadmium-free QDs as fluorescence label into lateral flow immunoassay for quantitative detection of C-reactive protein, and the limit of detection was 5.8 ng/mL, which was almost as low as that of cadmium-based quantum dot lateral flow test strip. Therefore, this kind of thick shell CIZS/ZnS//ZnS QDs can be used as probes for ultra-sensitive detection, and the further development of this kind of QDs has immense potential for future convenient and cost-effective in vitro cadmium-free nano-medical diagnostic kits.